Eggplant protects the heart during myocardial infarction
The eggplant, the deep purple vegetable that horticulturists want you to call 'fruit', contains substances that protect against a heart attack. By this we do not mean that eggplants help prevent a heart attack. According to an animal study, published in Food & Function in 2011, a diet with eggplants protects the heart muscle during a heart attack.
[FONT="]
[/FONT]

Study
[TABLE="width: 358, align: right"]
[TR]
[TD="align: right"][/TD]
[/TR]
[/TABLE]
Cardiologists from the University of Connecticut School of Medicine divided adult lab rats into 3 groups. For 30 days, the rats were fed standard chow [C], or chow to which the researchers added freeze-dried raw [R] eggplant or freeze-dried roasted eggplant [G].The researchers do not say how much eggplant they gave their lab animals.
Eggplants contain phenols such as caffeic acid, chlorogenic acid and nasunin. The latter substance gives the skin of aubergines their characteristic purple color. Roasting aubergines increases the amount of these phenols.
[FONT="]
[/FONT]

When the 30 days were up, the researchers stopped blood flow to the heart muscle for 30 minutes, imitating the effects of a heart attack. They then normalized the blood supply for 2 hours and measured how much damage the infarction had caused.
Results
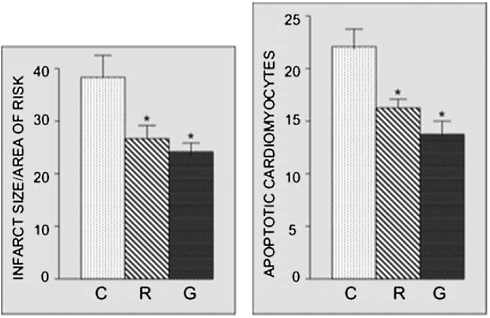
Eggplant supplementation reduced the damage caused by the artificial myocardial infarction. Eggplant reduced the area of damage in the heart muscle, and also reduced the number of heart cells that died.
[FONT="]
[/FONT]
Mechanism
The weird thing was, it didn't matter whether the rats got raw or roasted eggplant. Okay, roasting increased the amount of polyphenols in the aubergine, but that did not increase the protective effect of the vegetable.
So, for the time being, how eggplants exactly protect the heart during a heart attack remains a mystery .
Source:
Food Funct. 2011 Jul;2(7):395-9.
The eggplant, the deep purple vegetable that horticulturists want you to call 'fruit', contains substances that protect against a heart attack. By this we do not mean that eggplants help prevent a heart attack. According to an animal study, published in Food & Function in 2011, a diet with eggplants protects the heart muscle during a heart attack.
[FONT="]
[/FONT]

Study
[TABLE="width: 358, align: right"]
[TR]
[TD="align: right"][/TD]
[/TR]
[/TABLE]
Cardiologists from the University of Connecticut School of Medicine divided adult lab rats into 3 groups. For 30 days, the rats were fed standard chow [C], or chow to which the researchers added freeze-dried raw [R] eggplant or freeze-dried roasted eggplant [G].The researchers do not say how much eggplant they gave their lab animals.
Eggplants contain phenols such as caffeic acid, chlorogenic acid and nasunin. The latter substance gives the skin of aubergines their characteristic purple color. Roasting aubergines increases the amount of these phenols.
[FONT="]
[/FONT]


When the 30 days were up, the researchers stopped blood flow to the heart muscle for 30 minutes, imitating the effects of a heart attack. They then normalized the blood supply for 2 hours and measured how much damage the infarction had caused.
Results
Eggplant supplementation reduced the damage caused by the artificial myocardial infarction. Eggplant reduced the area of damage in the heart muscle, and also reduced the number of heart cells that died.
[FONT="]
[/FONT]

Mechanism
The weird thing was, it didn't matter whether the rats got raw or roasted eggplant. Okay, roasting increased the amount of polyphenols in the aubergine, but that did not increase the protective effect of the vegetable.
So, for the time being, how eggplants exactly protect the heart during a heart attack remains a mystery .
Source:
Food Funct. 2011 Jul;2(7):395-9.

