Age Related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
"Age-associated macular degeneration (AMD) involves the degeneration of the small central area of the retina, called macula, that controls visual acuity. AMD is a leading cause of vision loss in the elderly. In AMD, the macula is irreversibly destroyed, which leads to loss of vision required for activities such as driving, recognizing faces, reading, and seeing in color.The prevalence of AMD increases with age. The risk of getting AMD increases from 2% at 50–59 years of age to almost 30% at 75 years of age. The number of AMD cases is estimated to reach 196 million worldwide by 2020 and 288 million by 2040 if no effective treatment is developed."
"Here, we report the occurrence of AMD pathology and its prevention by chronic treatment with the neurotrophic peptidergic compound P021, in aged rats and 3xTg-AD mice."
"We found photoreceptor degeneration, lipofuscin granules, vacuoles, and atrophy in retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) as well as Bruch’s membrane (BM) thickening; in aged rats, we even found rosette-like structure formation. Microgliosis and astrogliosis were observed in different retinal layers. In addition, we also found that total tau, phosphorylated tau, Aβ/APP, and VEGF were widely distributed in the sub-retina of aged rats and 3xTg mice. Importantly, chronic treatment with P021 for 3 months in rats and for 18 months in 3xTg mice ameliorated the pathological changes above."
"These findings indicate the therapeutic potential of P021 for prevention and treatment of AMD and retinal changes associated with aging and Alzheimer’s disease."
Types of Age Related Macular Degeneration (Wet & Dry)
"There are two forms of AMD: a dry form and a wet form. The dry form, which is most common, is non-neovascular. It leads to atrophy of the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE), choriocapillaris, and photoreceptors. The wet AMD is neovascular. It occurs when new blood vessels invade from the choroid and penetrate Bruch’s membrane (BM), causing vascular leakage, hemorrhage, and scarring. Wet AMD is less common than the dry form but choroidal neovascularization (CNV) in this form leads to vision loss. Dry AMD is believed to result from the aging and thinning of macular tissues, deposition of pigment in the macula, or a combination of these two processes.AMD is a multifactorial disease, the etiopathogenesis of which probably involves several factors that are currently not understood. A growing body of evidence suggests that the immune system plays a key role in triggering neuroinflammation in the retina in AMD development. There are no early biomarkers to anticipate AMD, and no FDA-approved treatments are available, although a few are in clinical trials, and nutritional intervention may help prevent its progression from the dry to the wet form.
The retina is a part of the CNS and offers a direct window to cerebral pathology. Like brain, retina contains neurons, astroglia, microglia and microvasculature and participates in similar physiological activities and shows some of the similar neurodegenerative changes that have been reported in Alzheimer’s disease. The development of ocular biomarkers can potentially help AD drug discovery. AMD and AD share several similarities which include neurodegeneration, neuroinflammation, and accumulation of β-amyloid (Aβ) and hyperphosphorylated tau. AMD has also been referred to as AD of the eye."
Oral Peptide P21 Reduced Pathology of Age Related Macular Degeneration
“Female aged (19–21 months) Fisher rats (n = 7) were given P021 per os by gavage (10 ml/kg body weight) once a day for 88 days.”“AMD-like retinal pathology is reduced by P021 treatment in aged rats. (A) Experimental design to study the effect of P021 treatment on retina in aged rats. Fisher rats at age ~19–21 months received P021 in saline (500 nmoles/kg body weight/day, by gavage) or vehicle only for 3 months, whereas ~2- to 3-month-old rats received vehicle only for 3 months.”
"P021 is quite stable in artificial gastric juice (~90% for 30 min) and in artificial intestinal juice (>95% for 120 min). BBB studies on P021, which were carried out through a commercial service (APREDICA, Watertown, MA, USA), demonstrated that a sufficient amount of P021 crossed the BBB to exert its effect in the brain."
Acronyms for the picture captions of P21 statistics below:
"AMD, age-related macular degeneration; WT, wild type; 3xTg, triple-transgenic; AD, Alzheimer’s disease; RPE, retinal pigment epithelium; OS, outer segment; IS, inner segment; ONL, outer nuclear layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; GCL, ganglion cell layer. NFL, nerve fiber layer."Figure 1:
"AMD-like retinal pathology is reduced by P021 treatment in aged rats."
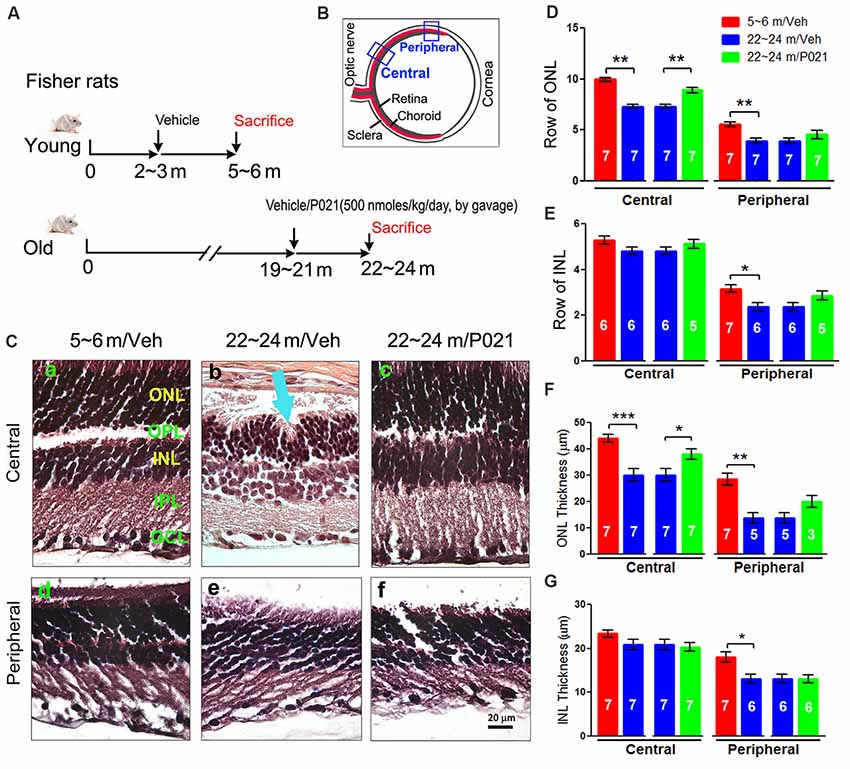
"(B) Schematic diagram showing the sections of the rat eye employed in the study. (C) Representative images of the central and peripheral retinas showing the morphology of retinal layers, H & E staining in 5-μm sagittal paraffin sections (Ca–f). Rosette-like rearrangements of photoreceptor cells that extend from the ONL and across the OPL toward INL (Cb), and photoreceptor inner segments (ISs) that project inward to form the core of the rosette (blue arrow) were found in ~22- to 24-month-old vehicle rats. (D–G) Quantification of rows and thickness of the ONL and INL in central and peripheral retina (n = 3–7 rats; exact “n” values are labeled in each bar)."
Figure 2:
"Chronic treatment with P021 reduces AMD-like pathology of RPE in aged rats. (A) H & E staining of RPE in the retina."
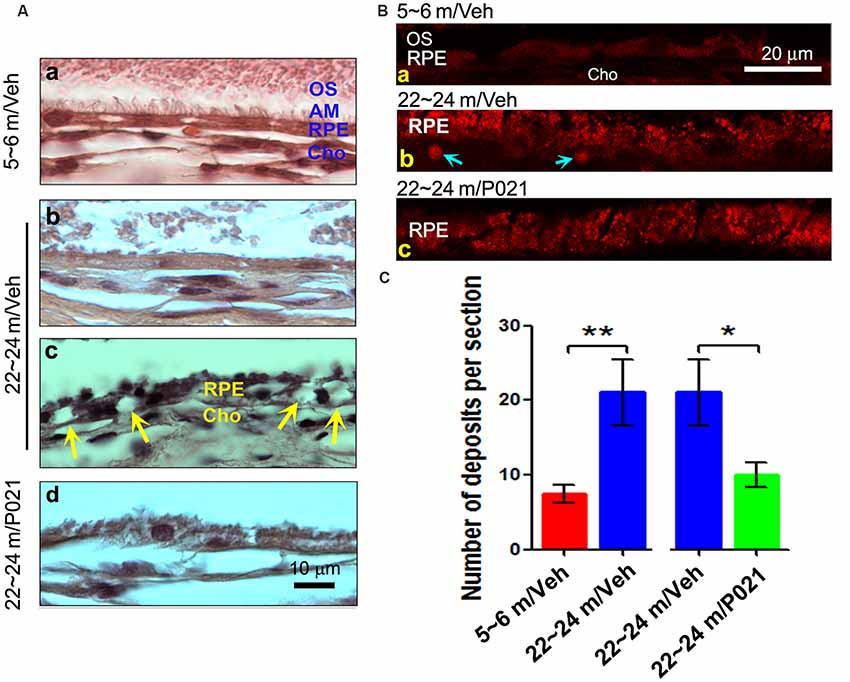
"The number of deposits between RPE and Cho (Bb, blue arrow), and lipofuscin granules were markedly greater in ~22- to 24-month-old/vehicle rats than in ~5- to 6-month-old/vehicle rats (Ba) or ~22- to 24-month-old/P021 rats (Bb,c)... AM was short or out of order, and atrophy and vacuolization of RPE (Ac, yellow arrow) were found in ~22- to 24-month-old/vehicle rats; no vacuolization was detected in other animal groups "
Figure 3:
"AMD-like retinal pathology is prevented by P021 treatment in aged 3xTg-AD mice."
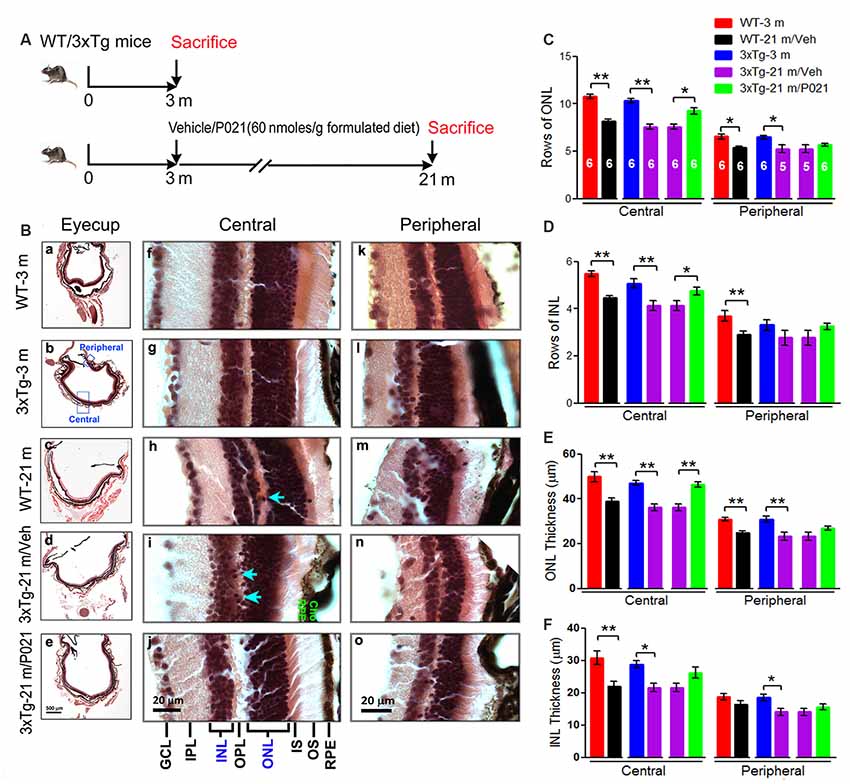
"(B) H & E staining to detect retinal morphology in 5-μm-thick sagittal paraffin sections; (a–e). The sagittal eyecup sections parallel to the axis from pupil to optic nerve; (b). Position of central and peripheral retinas are labeled in blue; (f–j). Representative images of central retina; (h,i). The extension of cell nuclei from the ONL to the INL (blue arrow); disruption and atrophy of RPE with increased brown lipofuscin granules (i green “RPE”); (k–o). Representative images of peripheral retina. (C–F) Quantification of rows and thickness of the ONL and INL in the central and peripheral retina (n = 5–6 mice; exact “n” values are labeled in each bar of panel (C)."
P021 Rescues the Retinal Pathology in Aged Fisher Rats
“When we previously evaluated the effect of chronic oral treatment with P021 on tau pathology and cognitive impairment in aged rats and mice, we did not observe any worsening in general physical state because of P021 treatment, suggesting a probable lack of any side effects.”“Photoreceptor cell loss was evaluated by analyzing the rows and thickness of the layers of photoreceptor cell nuclei (ONL). H & E staining showed that rows and thickness of ONL in the central and peripheral retinas were dramatically decreased in ~22- to 24-month-old rats (Figures 1C,D,F). P021 prevented these pathological changes more effectively in the central retina (Figures 1D,F) than in the peripheral retina (Figures 3D,F). There was also no significant difference between ~5- to 6-month-old rats and P021-treated ~22- to 24-month-old rats (Figures 1D,F), which suggests that P021 can prevent ONL lesions.”
“Also, the rows and thickness of INL in the peripheral retina were decreased in the ~22- to 24-month-old/Veh rats compared with the ~5- to 6-month-old/Veh rats, and ~22- to 24- month-old/P021 rats showed a clear trend to rescue the number of rows (Figures 1C,E,G)…”
“Additionally, we found that the laminar arrangement in the central retina in ~22- to 24-month-old/Veh rats was distorted by outer retinal folds and rosette-like structures (Figure 1Cb). These aberrations involved a semi-spherical organization of photoreceptor cell nuclei that occupied the ONL, extended across the outer plexiform layer (OPL), and encroached into the INL. The center of the rosettes appeared to be occupied by the photoreceptor inner segment (IS). No abnormal structure like this was observed in the ~5- to 6-month-old/Veh rats or ~22- to 24-month-old/P021 rats (Figures 1Ca,c,d,f).”
“Altogether, these results indicated photoreceptor cell degeneration in the central retina, and INL degeneration in the peripheral retina in ~22- to 24-month-old/Veh rats, and suggested that 3-month-long treatment with P021 protected ~19- to 21-month-old rats against AMD-like pathology in the central retina.”
P021 Rescues the Pathophysiology of RPE and BM in Aged Rats
“Dysfunction of the RPE presages photoreceptor cell loss, and the histological abnormalities in RPE are also a hallmark of human dry AMD.”“To investigate the histopathological changes in rats, the RPE layer was examined in sagittal sections stained with H & E. Apical microvilli (AM) in RPE were apparent in ~5- to 6-month-old/Veh rats (Figure 2Aa); in contrast, they were shortened or disorganized in the ~22- to 24-month-old/Veh rats (Figures 2Ab–d), and P021 treatment showed improvement in the arrangement of AM. Additionally, many RPE cells were vacuolated (Figure 2Ac, yellow arrows), and RPE atrophy (Figure 2Ac, yellow RPE) was detected in aged rats, whereas no apparent abnormalities were observed in the RPE of ~5- to 6-month-old/Veh rats and ~22- to 24-month-old/P021 rats (Figures 2Aa,d). Furthermore, many lipofuscin granules (Figures 2Ac,Bb) and deposits (Figures 2Bb,C) were present between RPE and Cho detected by auto-fluorescence in ~22- to 24-month-old/Veh rats, whereas very few lipofuscin granules were detected in ~5- to 6-month-old/Veh rats (Figures 2A,Ba); lipofuscin granules and deposition number were markedly decreased in ~22- to 24-month-old/P021 rats (Figures 2Bc,C). These results suggest that ~22- to 24-month-old/Veh rats exhibit RPE abnormalities, and P021 ameliorates these pathological changes.”
Chronic Treatment With P021 Can Prevent Retinal Lesions in Aged Mice
“We found that rows and thickness of ONL were all significantly decreased in the central retina in WT-21 m/Veh and 3xTg-21 m/Veh mice and that these changes in the central retina were prevented in 3xTg-21 m/P021 mice (Figures 3B,C,E). In the peripheral retina there was a significant decrease in rows and thickness of ONL in WT-21 m/Veh and only in the thickness but not in rows of ONL in 3xTg-AD-21 m/Veh, and P021 treatment showed a trend to rescue these changes (Figures 3C,E). Rows and thickness of INL in the central retina were also decreased in WT-21 m/Veh and 3xTg-21 m/Veh mice, and chronic treatment with P021 prevented these changes in 3xTg-21 m mice; although there was an obvious trend, the rescue of INL thickness by P021 treatment did not reach statistical significance (Figures 3B,D,F). The age-associated changes in rows and thickness of INL in the peripheral retina were smaller than those seen in the central retina, and their prevention by chronic treatment with P021 did not reach significance in 3xTg-21 m/P021 mice (Figures 3B,D,F). In addition, the nuclei of ONL in the central retina were extended across the OPL or protruded into the INL in the WT-21 m/Veh and 3xTg-21 m/Veh mice, which made the gap between the ONL and the INL narrower or unclear (Figures 3Bh,i), whereas this pathology was prevented in 3xTg-21 m/P021 mice (Figure 3Bj).”“Altogether, these findings indicated the degeneration of both the ONL and the INL in the central and peripheral retinas in WT/Veh and 3xTg/Veh mice at 21 months of age, and the prevention of these changes, especially in the central retina, by chronic treatment with P021 in 3xTg-AD mice.”
P021 Prevents RPE and BM Pathology in Aged Mice
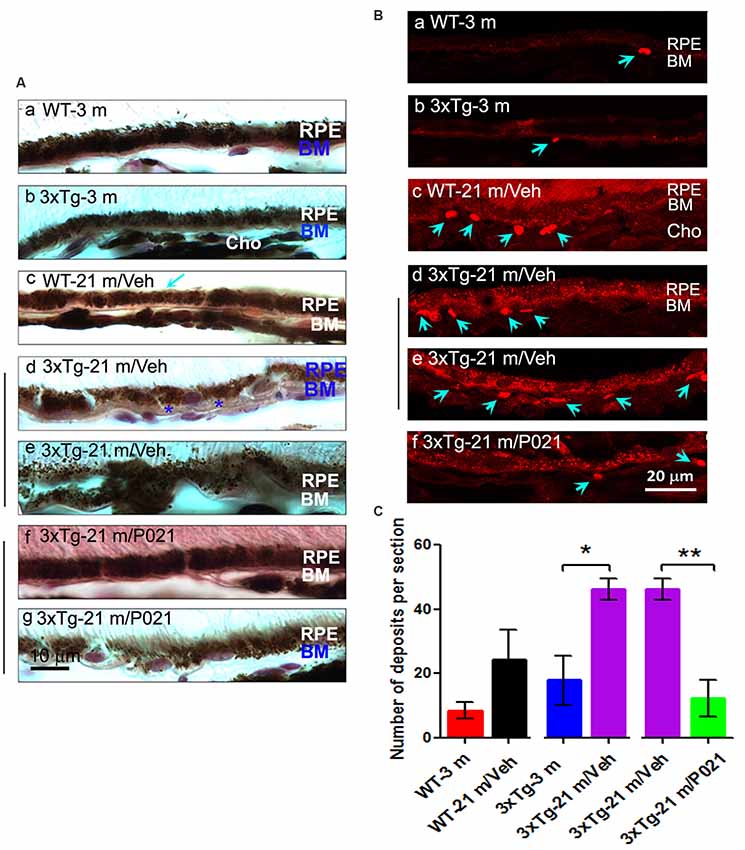
“Disruption and degeneration of RPE are well known to occur in AMD. We, therefore, investigated the occurrence of this pathology in both aged WT and 3xTg-AD mice and the effect of chronic treatment with P021 on its prevention. We found that the areas with the greatest photoreceptor disorganization were often associated with atrophied RPE and increases in lipofuscin granules in the central retina in 3xTg-21 m/Veh mice (Figure 3Bi). The central retina in WT-21 m/Veh and 3xTg-21 m/Veh mice showed multiple additional AMD features, including hypo-pigmentation, thinning, and disorganization of RPE (Figures 3Bi, 4Ad,e). RPE in 3xTg-21 m/Veh mice also showed frequent accumulation of large lipofuscin granules (Figures 3Bi, 4Ae). We found an increase in auto-fluorescence attributable to lipofuscin granules in the aged mice (Figures 4Bc,d,e). We also found thickening of the BM in 3xTg-21 m/Veh mice (Figure 4Ad) compared to young and old WT mice Figures 4Aa–c while there was no BM thickening in 3xTg-21 m/P021 mice (Figures 4Aa,g). Deposits between the RPE and Cho were detected by auto-fluorescence in 3xTg-21 m/Veh mice, much more than in WT-21 m/Veh mice (Figures 4Bd,e); WT-3 m or 3xTg-3 m mice controls, however, showed very few deposits (Figures 4Ba,b). The number of deposits was increased both in WT-21 m/Veh and 3xTg-AD-21 m/Veh mice though in the former it did not reach significance due to large standard error (Figure 4C). The deposits were significantly reduced in 3xTg-21 m/P021 mice, although some small lipofuscin granules could still be observed (Figure 4Bf). Together, our data indicate that aged mice, especially 3xTg-21 m/Veh mice, exhibit RPE and BM abnormalities that highly resemble human dry AMD.”“Most of these AMD features were prevented by chronic treatment with P021 administered in the diet.”
Figure 4:
“Chronic treatment with P021 prevents AMD-like features of RPE in aged mice.”
P021 Reduces Microgliosis in the Retina of Aged Mice and Rats
“In AMD, activated microglia are localized in the ONLs where they are associated with photoreceptor degeneration, apparently for the removal of cell debris. We used Iba-1 immunofluorescence to study microgliosis in the retina of aged mice and rats.”“Interestingly, the Iba-1 immunostaining in 3xTg-21 m/Veh mice was significantly higher than in WT-21 m/Veh mice, whereas it was decreased in 3xTg-21 m/P021 mice to the levels in WT-3 m/Veh and 3xTg-3 m/Veh mice in the peripheral retina (Figure 5B), even though there was no obvious difference in the distribution of Iba-1–positive staining (Figures 5Af–j).”
Figure 5:
“P021 reduces microgliosis in the retinas of aged mice and rats.”
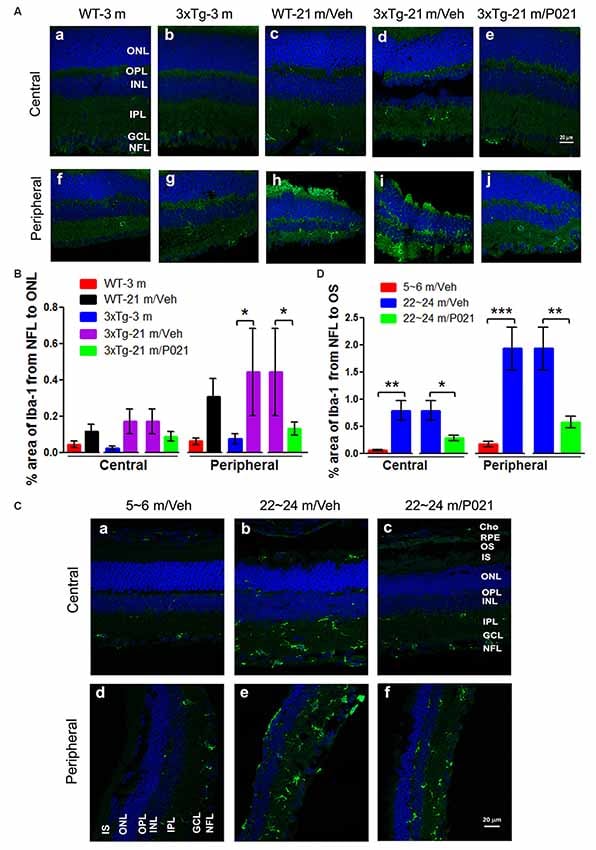
“Quantitatively, the relative Iba-1 immunostaining from the NFL to the OS in the central and peripheral retinas of ~22- to 24-month-old/Veh rats was increased significantly in ~22- to 24-month-old/Veh rats as compared to ~5- to 6-month-old/Veh rats, and P021 treatment dramatically reduced it in ~22- to 24-month-old rats (Figure 5D).
Altogether, these findings indicate that microglia are distributed more widely in the whole retina of aged mice and rats, especially in the ONL, which is associated with photoreceptor degeneration (shown in Figures 1, 3), and that treatment with P021 can efficiently protect the retina from inflammatory damage in aged mice and rats.”
P021 Reduces Astrogliosis in the Retina of Aged Mice and Rats
“To study the localization of astrogliosis and the response to P021 treatment in the retina of aged mice and rats, astrocytic/Müller cell activation was evaluated by immunostaining with anti-glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP).”“In contrast, the GFAP-positive staining was limited to the NFL and GCL in 3xTg-21 m/P021 mice (Figures 6Ae,j). The area percentage of GFAP from the NFL to the ONL in the central retina of 3xTg-21 m/Veh mice was significantly higher than in 3xTg-3 m mice and WT-21 m/Veh mice and was reduced by P021 treatment to the levels in WT-3 m/Veh and 3xTg-3 m/Veh mice (Figure 6B).”
Figure 6:
“P021 reduces astrogliosis in the retinas of aged mice and rats.”
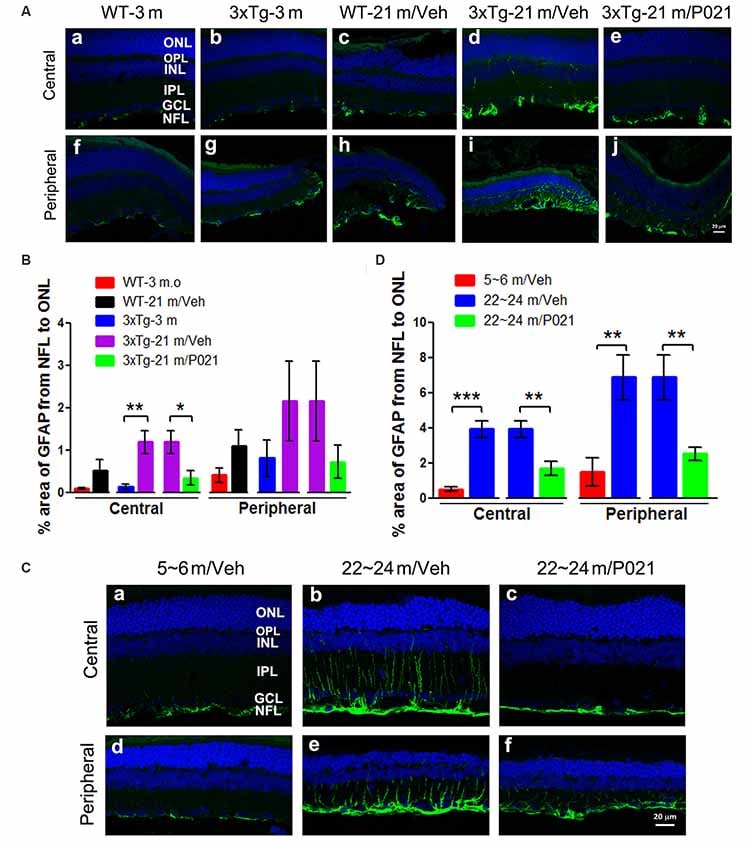
“The GFAP staining was reduced very much in ~22- to 24-month-old /P021 rats as compared to ~22- to 24-month-old/Veh rats (Figures 6Cc,f). The area percentage of GFAP-positive staining was also drastically elevated in the central and peripheral retinas in ~22- to 24-month-old/Veh rats as compared to ~5- to 6-month-old/Veh rats and ~22- to 24-month-old/P021 rats (Figure 6D).
Altogether, the above findings indicate that P021 can prevent and rescue microgliosis and astrogliosis in the retina of both aged 3xTg-mice and aged rats.”

